Excel How To Find Unique Values In A List
Author: Oscar Cronquist Article last updated on September 27, 2021
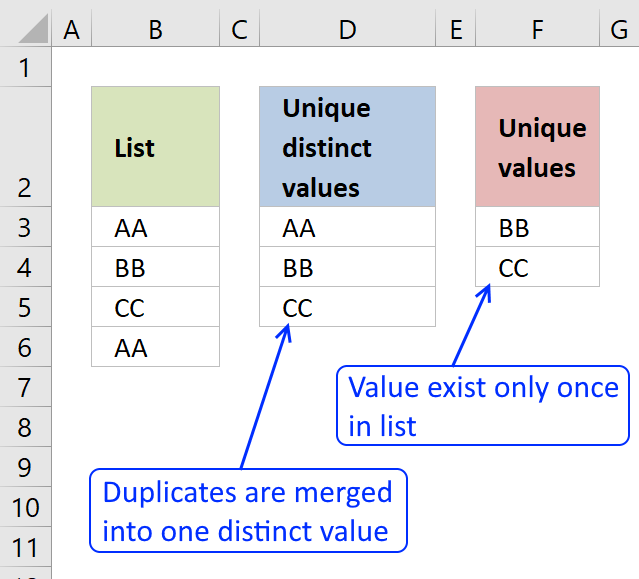
Offset, let me explain the difference betwixt unique values and unique distinct values, information technology is of import you know the divergence so yous can find the data y'all are looking for on this web page.
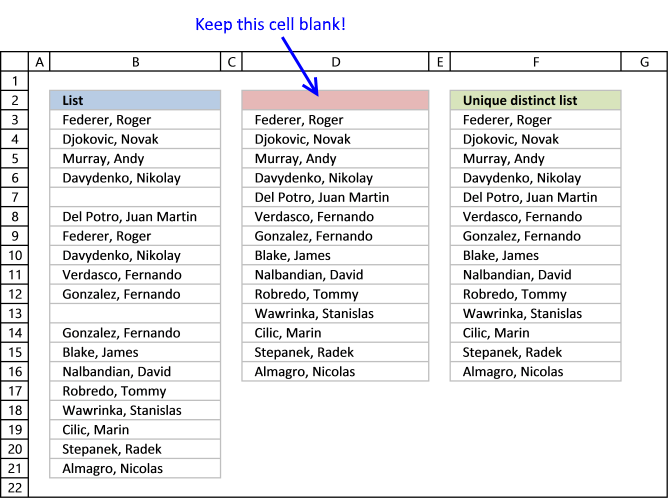
The picture in a higher place shows a list of values in column B, note value AA has a indistinguishable. Unique singled-out values are all jail cell values just indistinguishable values are merged into one distinct value. In other words, duplicates are removed just one instance of each value is left in the list.
Column F contains unique values from column B, pregnant values that exist only one time in column B. Value AA is non in column F considering it has a duplicate, in other words, AA is not unique in cavalcade B. To filter duplicates, read this post: Extract a list of duplicates from a column
Table of Contents
Working with unique distinct values
- How to extract unique distinct values from a column [Formula]
- Video
- Copy unique distinct values
- Explaining formula
- Get Excel file
- Excerpt unique distinct values (instance sensitive) [Formula]
- Video
- Explaining formula
- Become Excel file
- Filter unique distinct values [Advanced Filter]
- Video
- Re-create unique distinct values to another location
- Filter unique distinct values, in place
- Highlight unique distinct values [Conditional Formatting]
- Video
- Explaining formula
- Sort Conditional formatted cells at the top
- How to hide duplicate values [Conditional Formatting]
- Put unique singled-out values at the top of the list [Provisional Formatting]
- Excerpt unique distinct sorted values from a jail cell range [UDF]
- Video
- How to create an assortment formula
- VBA code
- Where to put the code?
- Filter unique distinct values from multiple sheets [Add-In]
- Video
- How to extract unique distinct values from a column [Erstwhile array Formula]
- How to create an array formula
- Explaining formula
Excerpt unique distinct values - Pivot Table (Link)
Working with unique values
-
-
- How to filter unique values from a list [Formula]
- Explaining formula
- Get Excel file
- Highlight unique values [Provisional Formatting]
- Video
- Sort unique values at the top
- How to filter unique values from a list [Formula]
-
Tips and tricks
-
- Useful tips
- Excel defined tables
- Named ranges
- Remove errors, Excel version 2007 and later
- Remove errors, Excel version 2003 and earlier
- How to ignore blank cells
- Video
- Get Excel file
- Useful tips
- What you volition learn in this article
- What is possible with formulas?
- What is the easiest fashion to filter unique distinct values?
What y'all will larn in this article
- The difference between unique distinct values and unique values.
- How to decide which Excel feature to use.
- How to use a formula that extracts unique distinct values.
- How to copy the values returned past the formula.
- How the formula works and the functions being used.
- How to filter unique singled-out values considering lowercase and capital letters.
- How to filter unique distinct values using the Avant-garde Filter.
- How to highlight unique distinct values using Conditional Formatting.
- How to build a User defined Part that filters unique distinct values sorted from A to Z.
- Where to put the VBA code.
- How to enter and utilise the User defined Function.
- How to filter unique values using a formula.
- How to highlight unique values using Conditional Formatting.
Back to top
What is possible with formulas?
You have quite a few options to cull from if yous are looking for a fashion to create a unique distinct list in your workbook, all demonstrated in this mail or on this website. Not only an uncommonly small regular formula, if you want to apply that, but also awesome born features in Excel that makes your work then much easier.
Formulas are very versatile, they permit y'all to build solutions for very specific tasks like filtering unique distinct values from two separate columns or three. If your list contains blanks and then this commodity is for you: Excerpt a unique singled-out list and remove blanks
Perhaps you desire to exercise a wildcard lookup and return unique distinct values or simply return unique singled-out values based on a condition.
I have as well written articles that explains how to create a unique distinct list sorted alphabetically, sum or frequency.
There is also a formula for extracting unique singled-out values located in a multi-column cell range, it is a somewhat more complicated assortment formula, yet, there is a custom part as well, if you prefer that.
Back to summit
What is the easiest way to filter unique distinct values?

I would choose the advanced filter if you are not looking for a formula. It lets yous quickly filter a unique distinct list.
If you lot know that you will be extracting unique singled-out values from fourth dimension to time, like in a dashboard or an interactive worksheet, I recommend using a formula and an Excel divers table. Yous won't need to echo the same steps over and over compared to the advanced filter and that volition salve you lot time and repetitive work.
Nonetheless working with a large data set up may slow downward the formula calculations considerably depending on your computer hardware, so perhaps the User Defined Function [UDF] is a better option or even better a pin tabular array, if you have huge amounts of information to work with.
The Excel Pivot table is lightning fast even with huge information tables just it does have a little learning curve and information technology requires a few steps to set it up but in my opinion, it is totally worth learning how to use pivot tables. You will be surprised how easy information technology is to beginning working with Excel Pivot tables.
Provisional Formatting allows you to format cells determined by a built-in dominion or a formula y'all construct. In this post, you lot volition find a Conditional Formatting formula that highlights unique and unique distinct values. Did y'all know that yous tin can easily sort highlighted values on top? Check out conditional formatting.
I have made an add-in that lets yous excerpt unique, unique distinct and indistinguishable values and records from multiple worksheets. This allows yous to easily join data from multiple sources in your workbook.
There is also a useful array formula in this article that extracts a instance-sensitive unique singled-out listing, this is a special case which the congenital-in Excel tools can't achieve.
Back to top
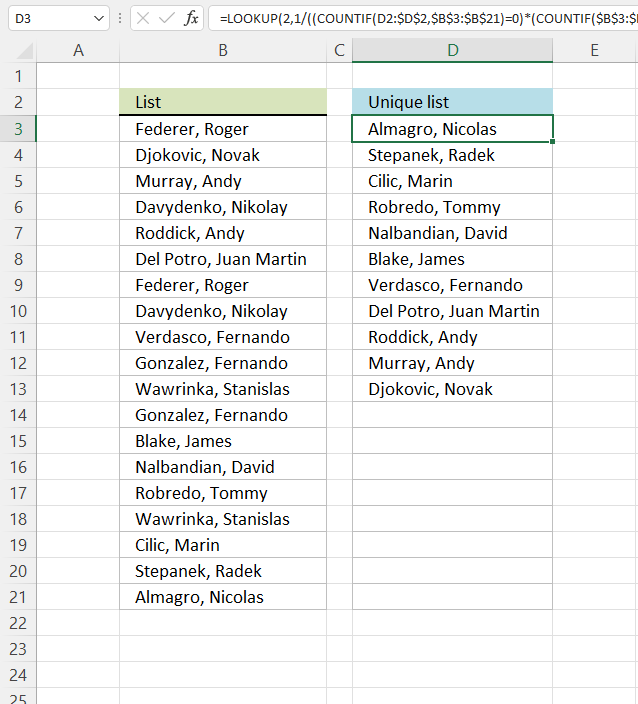
1. Create a list of unique singled-out values
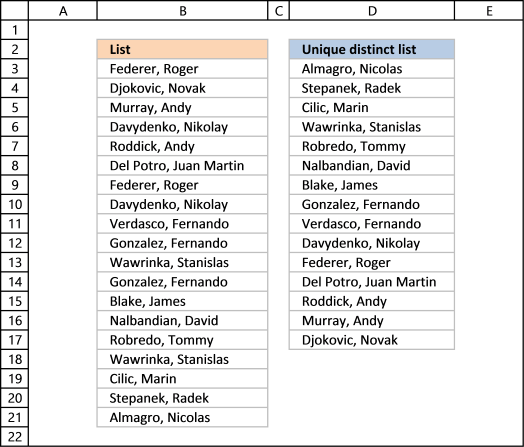
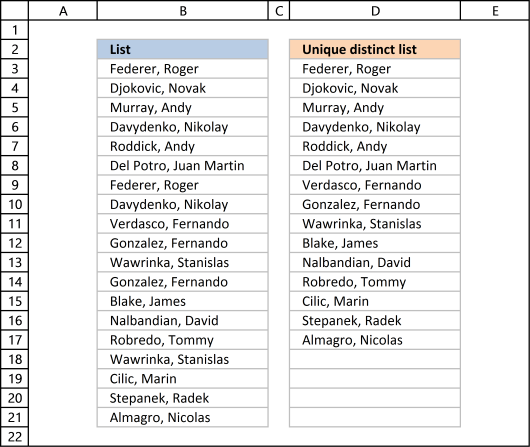
Column B contains names, some cells take duplicate values. A formula in cavalcade D extracts a unique distinct list from column B.
Update: 2017-08-15!
This formula is even smaller than the array formula and you are not required to enter this as an array formula. The following formula is for older Excel versions than Excel 365 subscribers.
Formula in jail cell D3:
=LOOKUP(2,1/(COUNTIF($D$2:D2,$B$3:$B$21)=0),$B$3:$B$21)
I will explain how this formula works in the video below and in section ane.iii also below.
Back to tiptop
Update: 2020-05-28!
Microsoft Excel released new functions for Excel 365 subscribers in January 2020. I of those new functions is the UNIQUE function, it allows y'all to easily extract a unique singled-out list using just one function.
Formula in cell D3:
=UNIQUE(B3:B21)
This formula is entered equally a regular formula, nonetheless, it is a dynamic array formula. Microsoft Excel introduced dynamic array formulas in January 2020 as well.
Dynamic array formulas expand to cells beneath automatically if more than than ane value is returned from the formula. Microsoft Excel calls this behavior spilling. You lot can discover more example of the UNIQUE role hither.
I volition draw a formula for older Excel versions below.
Excerpt unique singled-out values - Excel 365 (Link)
Extract unique distinct values sorted from A to Z - Excel 365 (Link)
Extract unique distinct values ignoring blanks - Excel 365 (Link)
Extract unique singled-out values sorted from A to Z ignoring blanks - Excel 365 (Link)
one.1 Video
This video demonstrates how to use the formula:
Subscribe to Get Digital Assist on Youtube:
Back to top
1.2 Copy unique singled-out values
To copy unique distinct values to some other location you must brand sure you re-create the values and not the formula:
- Select listing
- Copy list, shortcut keys: CTRL + C or press this button:
- Printing with right mouse push button on on destination prison cell and printing with left mouse push button on the black pointer next to "Paste Special..."
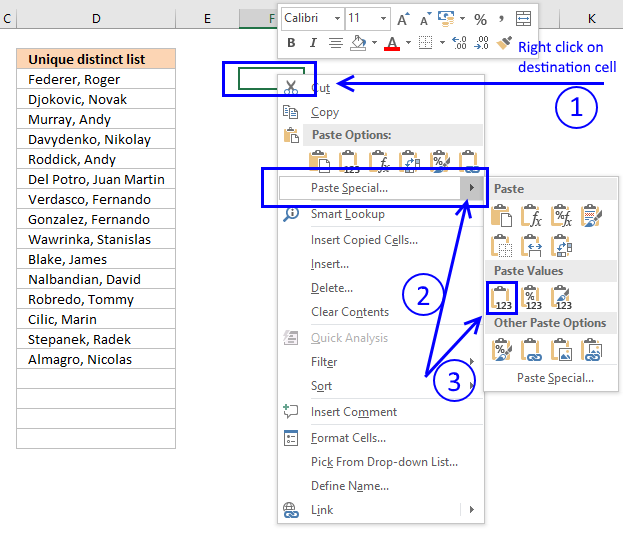
- Then press with left mouse button on "Paste Values" push button.
Back to top
1.3 Explaining formula in cell D3
Footstep 1 - Count previous values above the current prison cell
The COUNTIF function allows you to count values based on a status. With the help from an expanding cell reference, the formula knows which of the values that have been extracted.
In prison cell D3 no values have been extracted then information technology compares the value in the jail cell above current cell, this happens to be the Header value. Brand sure yous don't accept a value in the list that matches the header value, it won't be extracted.
COUNTIF($D$ii:D2,$B$three:$B$21) is entered in cavalcade F, displayed in the film beneath.
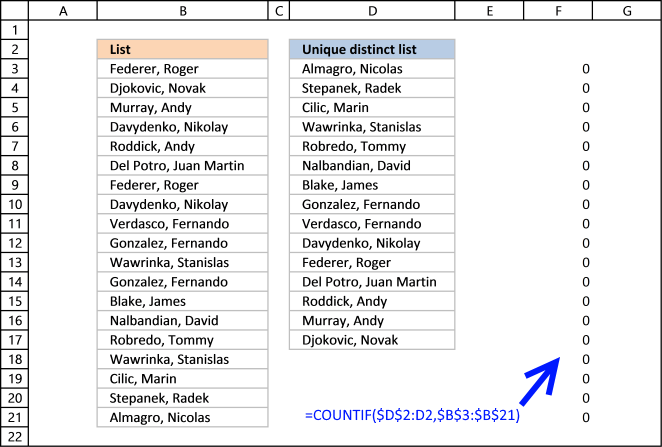
The value in jail cell D2 is not found in any instance in cell range B3:B21, all values in the array are 0 (naught). Note that the array has the aforementioned size equally the list in column B, xix values.
Pace 2 - Compare assortment with 0 (zilch)
To identify values that have non been shown the formula compares the array with 0 (zero) and the consequence are boolean values (TRUE or FALSE) for each value in the array.
COUNTIF($D$2:D2,$B$3:$B$21) = 0
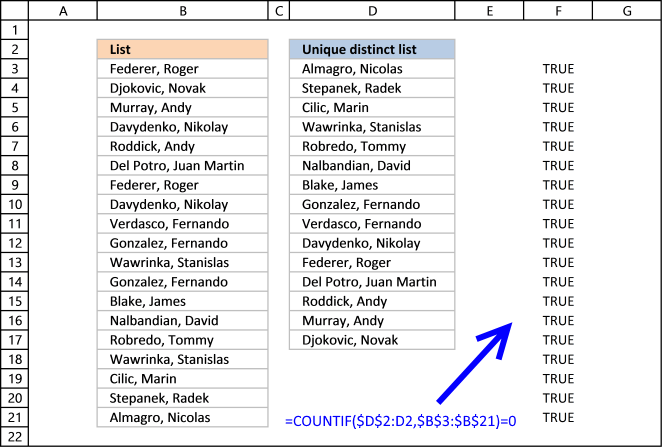
The array contains 19 boolean values, all TRUE.
Step iii - Divide ane with array
The boolean value True is equal to 1 and FALSE is equal to 0. If a value in the assortment is True the result will be 1 because 1/True equals 1.
If a value in the array is FALSE the issue will be #DIV0! considering 1/Imitation is ane/0 and you tin can't divide a number with zero. Excel returns an error.
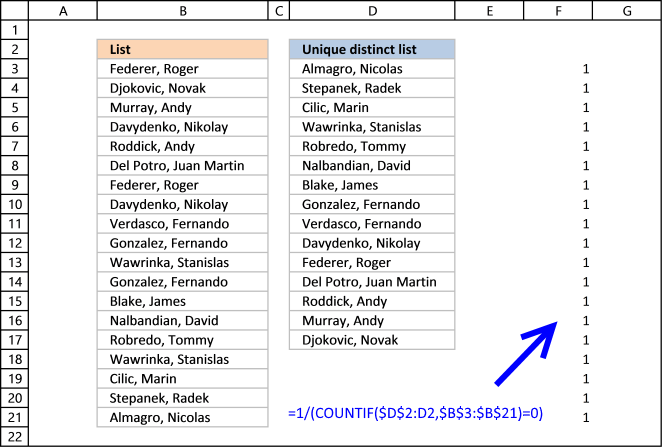
The practiced thing about the LOOKUP role is that information technology ignores errors, run across next footstep.
Footstep 4 - LOOKUP value
The LOOKUP function is designed to piece of work with sorted cell ranges or arrays, you become weird results if they are non sorted. Be conscientious using the LOOKUP function.
Nonetheless, in this case, the values in the array are either 1 or #DIV0!. Surprisingly it ignores errors, the merely matter information technology can discover then is a value that is 1.
The first statement in the LOOKUP part is two then the function finds the terminal largest value that is equal to ii or smaller.
LOOKUP(2,i/(COUNTIF($D$2:D2,$B$3:$B$21)=0),$B$three:$B$21)
becomes
LOOKUP(2,{i;1;1;i;1;1;1;1;1; 1;1;ane;i;one;i;i;1;1;ane},$B$3:$B$21) and matches the concluding value in the array. LOOKUP role then returns the corresponding value in cell range $B$3:$B$21 which is Almagro, Nicolas
Back to height
i.four Excel file
Extract a unique singled-out list sorted from A to Z
Excerpt a unique distinct list sorted from A to Z ignore blanks
Vlookup – Return multiple unique distinct values
Unique distinct list sorted alphabetically based on a condition
Extract a unique distinct listing from 2 columns
Excerpt a unique singled-out list from three columns
Filter unique distinct records
Back to top
ii. Excerpt a unique distinct list (case sensitive)
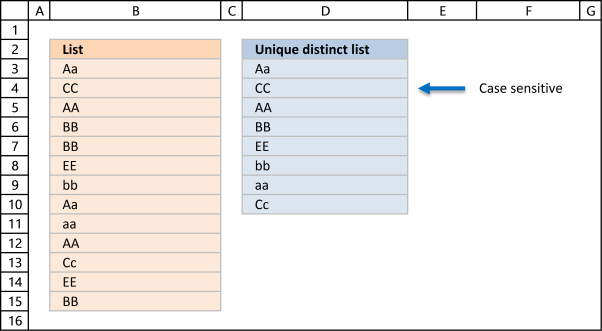
The following array formula lists unique distinct values from a list also considering upper and lower letters. For case, the value "Aa" is non equal to "AA".
Array formula in cell D3:
=INDEX($B$iii:$B$15, MATCH(0, FREQUENCY(IF(EXACT($B$3:$B$15, TRANSPOSE($D$ii:D2)), Match(ROW($B$iii:$B$15), ROW($B$three:$B$fifteen)), ""), MATCH(ROW($B$iii:$B$15), ROW($B$3:$B$xv))), 0))
Excel 365 subscribers can apply this regular somewhat shorter formula in cell D3 than the formula below:
=LET(z, B3:B15, x, SEQUENCE(z), Alphabetize(z, MATCH(0, FREQUENCY(IF(EXACT(z, TRANSPOSE($D$two:D2)), x, ""), 10), 0))
The formula above contains two new formulas: LET function and the SEQUENCE function.
This article explains the formula: Excerpt a instance sensitive unique list from a column - Excel 365
2.1 Video
This video demonstrates how to build a formula that extracts a case-sensitive unique distinct listing:
Subscribe to Get Digital Help on Youtube:
This mail shows yous how to excerpt a example sensitive unique list from a column:
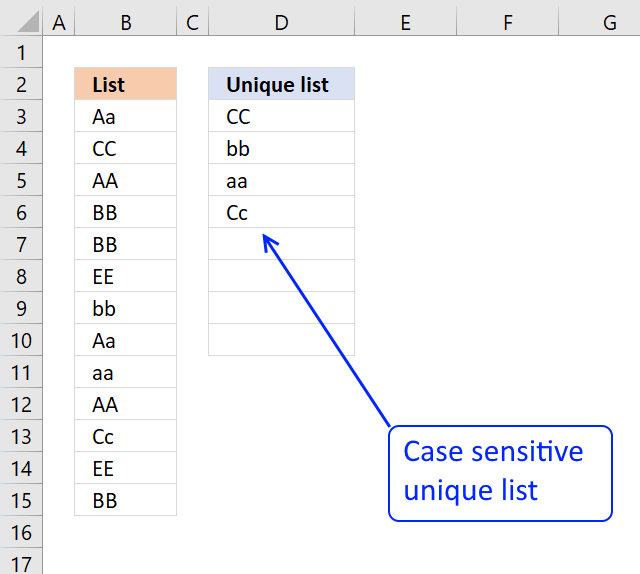
How to excerpt a case sensitive unique list from a column
How to enter an assortment formula
Dorsum to top
2.2 Explaining the array formula in cell C3
Footstep one - Transpose previous values
TRANSPOSE($D$2:D2)
becomes
TRANSPOSE({"Unique distinct list (case sensitive)";"Aa"})
and returns
{"Unique distinct list (example sensitive)","Aa"}
Notation that the ; (semicolon) changes to a , (comma)
Recommended reading:
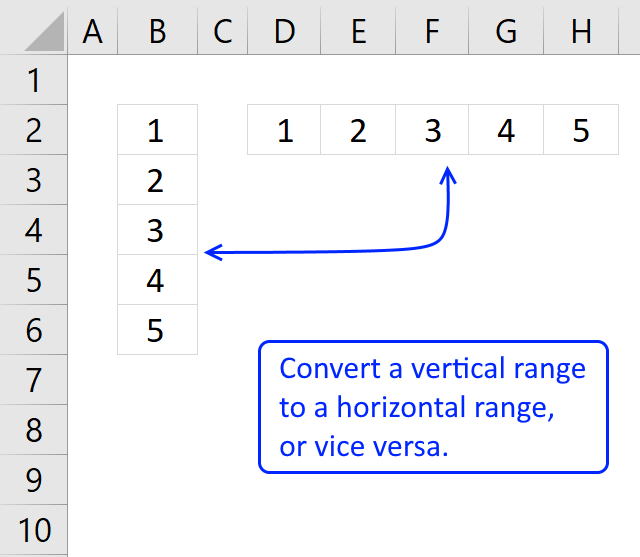
How to apply the TRANSPOSE function
Step ii - Check if two text strings are exactly the same, also instance sensitive
EXACT($B$3:$B$15, TRANSPOSE($D$2:D2))
becomes
Exact($B$3:$B$15, TRANSPOSE({"Unique distinct list (case sensitive)","Aa"})
becomes
EXACT($B$iii:$B$15, TRANSPOSE({"Unique distinct list (case sensitive)","Aa"})
becomes
EXACT({"Aa"; "CC"; "AA"; "BB"; "BB"; "EE"; "bb"; "Aa"; "aa"}, TRANSPOSE({"Unique distinct list (case sensitive)","Aa"})
and returns
{FALSE, TRUE; FALSE, FALSE; FALSE, FALSE; Faux, FALSE; FALSE, False; FALSE, FALSE; FALSE, Fake; Fake, True; FALSE, FALSE}
Stride 3 - Render relative position in array if True
IF(Exact($B$3:$B$15, TRANSPOSE($C$one:C1)), MATCH(ROW($B$iii:$B$15), ROW($B$3:$B$15))
becomes
IF({False, TRUE; FALSE, FALSE; Imitation, FALSE; FALSE, False; FALSE, False; FALSE, False; Faux, False; FALSE, TRUE; Fake, False}, Match(ROW($A$1:$A$nine), ROW($A$i:$A$9)))
becomes
IF({Imitation, Truthful; FALSE, FALSE; FALSE, FALSE; FALSE, Imitation; Faux, FALSE; FALSE, Simulated; FALSE, FALSE; FALSE, Truthful; Simulated, Imitation}, {i;2;3;iv;5;half dozen;7;eight;9})
and returns
{Fake,1; Imitation,False; Fake,FALSE; FALSE,Faux; FALSE,FALSE; FALSE,False; Simulated,Fake; FALSE,8; FALSE,Faux}
Recommended article:
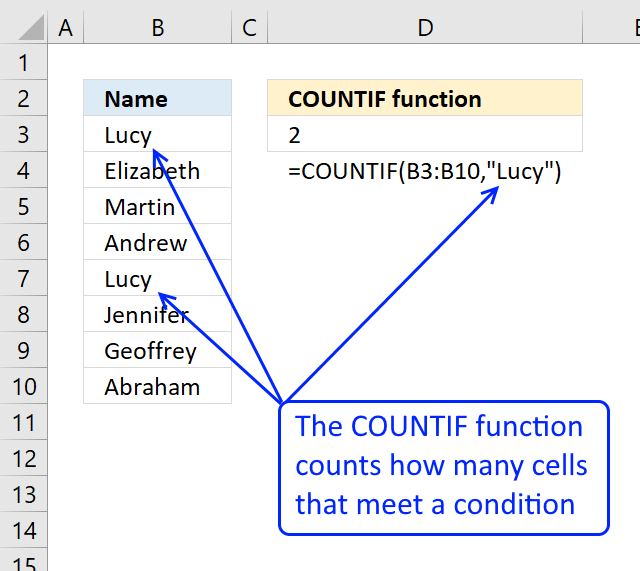
How to apply the COUNTIF office
Step 4 - Calculate how often values exist in an array
FREQUENCY(IF(Verbal($B$3:$B$15, TRANSPOSE($C$1:C1)), Lucifer(ROW($B$3:$B$xv), ROW($B$3:$B$fifteen)), ""), MATCH(ROW($B$iii:$B$15), ROW($B$3:$B$15)))
becomes
FREQUENCY({FALSE,ane; False,False; FALSE,Imitation; Simulated,False; FALSE,FALSE; Faux,FALSE; Imitation,Simulated; FALSE,8; FALSE,FALSE},Match(ROW($B$3:$B$xv),ROW($B$3:$B$15)))
becomes
FREQUENCY({Imitation,1; Faux,Simulated; Imitation,False; Faux,Simulated; FALSE,FALSE; Faux,FALSE; FALSE,Simulated; Faux,8; Simulated,False},{i;2;iii;iv;five;vi;7;viii;9})
and returns
{1;0;0;0;0;0;0;i;0;0} Aa is establish in position 1 and 8 in prison cell range $B$three:$B$15
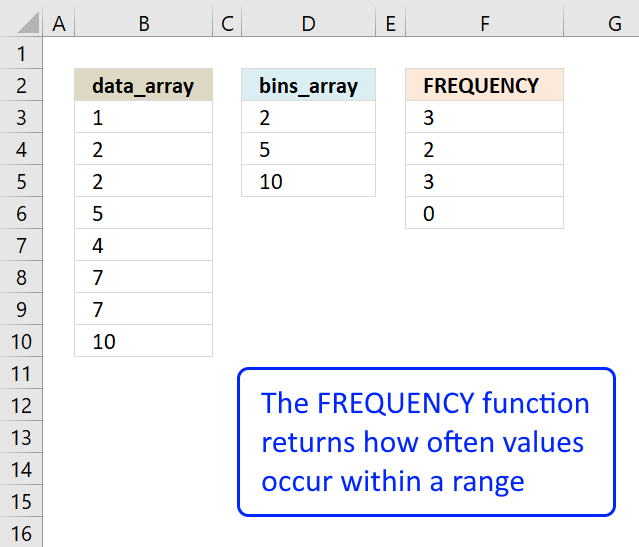
How to use the FREQUENCY role
Step 5 - Find get-go empty value (0) in array
Friction match(0, FREQUENCY(IF(Verbal($B$iii:$B$15, TRANSPOSE($C$1:C1)), MATCH(ROW($B$3:$B$fifteen), ROW($B$3:$B$fifteen)), ""), MATCH(ROW($B$3:$B$15), ROW($B$3:$B$15))), 0)
becomes
Friction match(0, {1;0;0;0;0;0;0;i;0;0}, 0)
and returns 2.
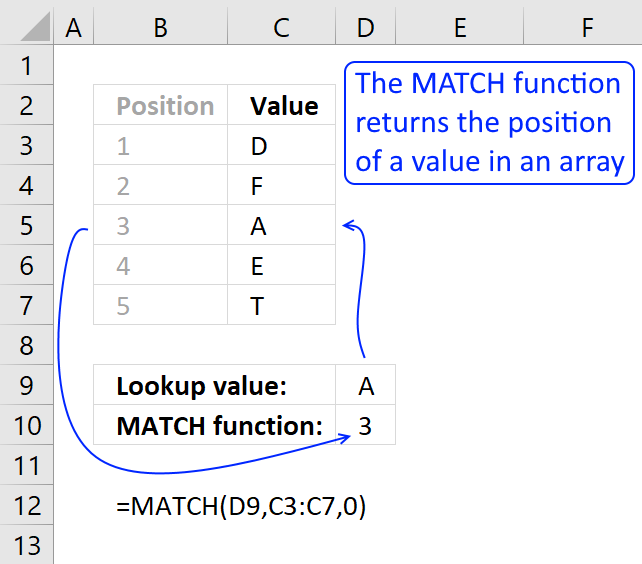
How to use the MATCH role
Step 6 - Return value from position 2
Index($B$3:$B$15, Match(0, FREQUENCY(IF(EXACT($B$3:$B$15, TRANSPOSE($C$1:C1)), Match(ROW($B$3:$B$15), ROW($B$iii:$B$fifteen)), ""), MATCH(ROW($B$three:$B$15), ROW($B$3:$B$xv))), 0))
becomes
INDEX($B$iii:$B$15, ii)
and returns "CC" in cell C3.
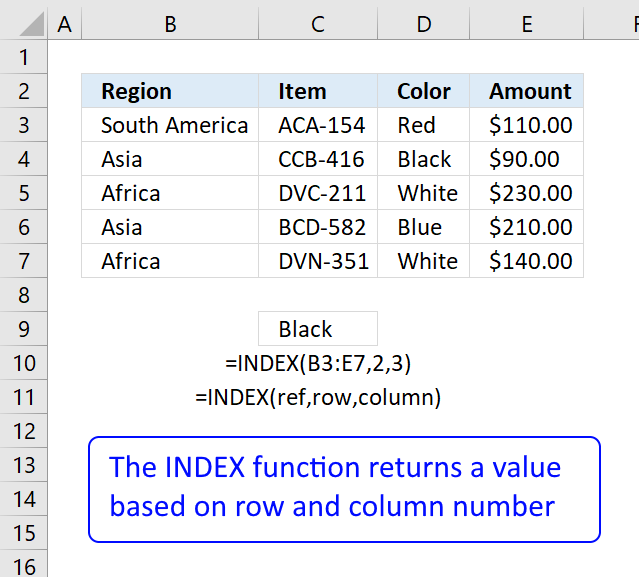
How to employ the Alphabetize function
Back to top
two.3 Excel file
Back to elevation
Recommended articles
Case sensitive lookup and return multiple values
Filter values based on a status - case sensitive (Excel 365)
Filter unique distinct values (instance sensitive) [UDF]
Filter unique singled-out records (case sensitive) [UDF]
Back to peak
iii. Extract unique singled-out values [Advanced Filter]
First a little reminder, unique distinct values are all cell values but duplicate values are merged into one singled-out value.

3.1 Video
The following video shows y'all how to filter unique singled-out values using Avant-garde Filter:
Subscribe to Get Digital Assist on Youtube:
Back to height
3.ii Instructions - Copy unique distinct values to another location
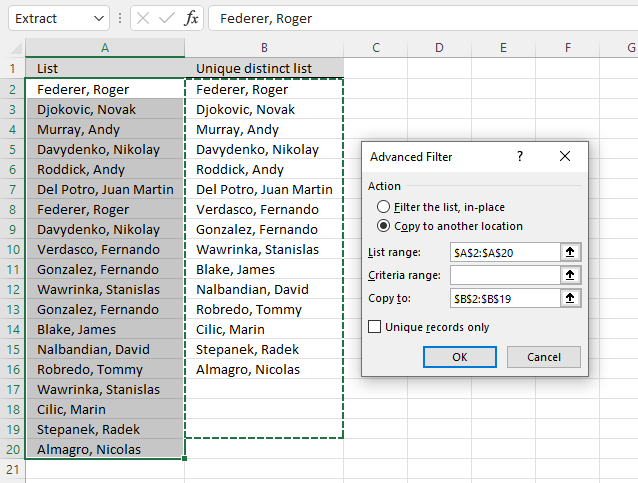
This section describes how to extract unique distinct values using the built-in feature "Advanced Filter".
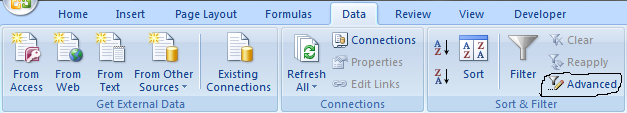
- Go to tab "Data" on the ribbon.
- Printing the "Advanced Filter" push button on the ribbon.
- Press button "Copy to another location".
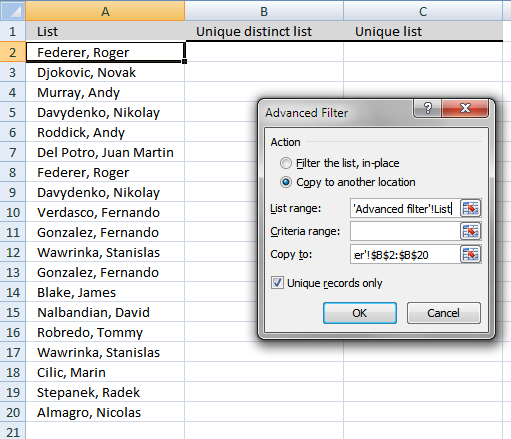
- Press "List range:" and select range to filter unique distinct values.
- Press "Copy to: and select a range.
- Press "Unique records only" button to select information technology.
- Printing with left mouse button on "OK" button to apply settings and start extracting.
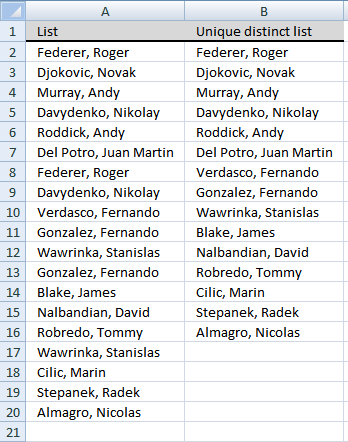
Back to tiptop
3.three Instructions - Filter unique distinct values, in identify
If you choose to filter unique singled-out values in-identify, press with left mouse button on the first choice button in the dialog box.
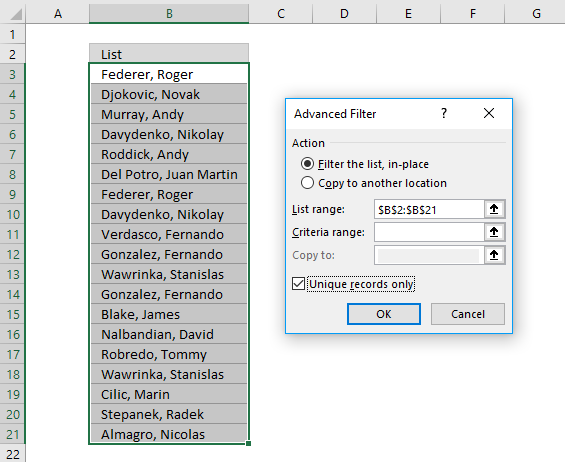
You can and so select unique distinct values and paste to some other location, indistinguishable values are hidden and are ignored when yous re-create cell range B3:21 and paste to a new location, very useful.
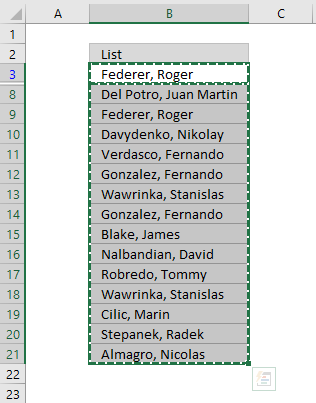
The pic beneath shows you the selected distinct values subsequently I cleared the Advanced Filter, duplicate values are not selected considering they were subconscious.
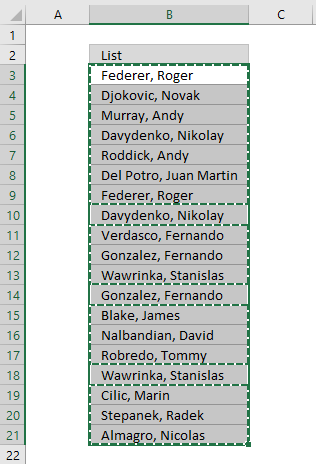
Recommended articles
Lookup and return multiple values [Advanced Filter]
Extract all rows that meet critera in one column [Advanced Filter]
An Advanced Filter is not the just powerful congenital-in feature in Excel, I highly recommend that you acquire pivot tables. Possibly the most powerful tool but too the to the lowest degree known:
How to use Pivot Tables – Excel's most powerful characteristic and also least known
The Excel divers table is also extremely useful, it allows you lot to speedily sort, filter and manipulate data. Larn that and much more:
How to use Excel Tables
An Excel table allows you to hands sort, filter and sum values in a data set where values are related.
How to utilise Excel Tables
Dorsum to elevation
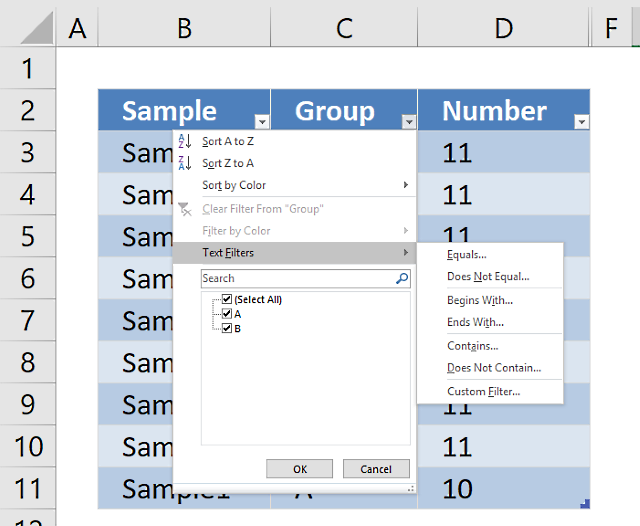
This section demonstrates how to highlight unique singled-out values using Excel'south congenital-in feature "Conditional Formatting".
The image shows you unique singled-out values highlighted using Conditional Formatting.
four.1 Video
This video demonstrates how to highlight unique singled-out values:
Subscribe to Get Digital Help on Youtube:
How to highlight unique singled-out values
- Select cell range B3:B21.
- Go to tab "Home" on the ribbon.
- Press on "Conditional Formatting" button.
- Press on "New Dominion...".
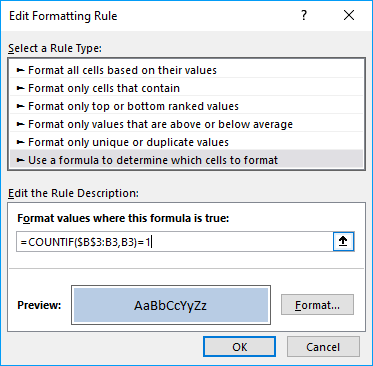
- Press on "Apply a formula to determine which cells to format:".
- Type this formula: =COUNTIF($B$three:B3,B3)=1
- Press on "Format..." push.
- Pick a color.
- Printing OK button.
- Press OK button again.
Back to top
4.2 Explaining Provisional Formatting formula
A CF formula works somewhat differently than a regular formula, however, they may be harder to spot.
It is possible that you can't even see if a cell range has CF practical to it or non, if no cells are highlighted.
I recommend that you copy the CF formula and enter it to an adjacent column to ameliorate show how they work.
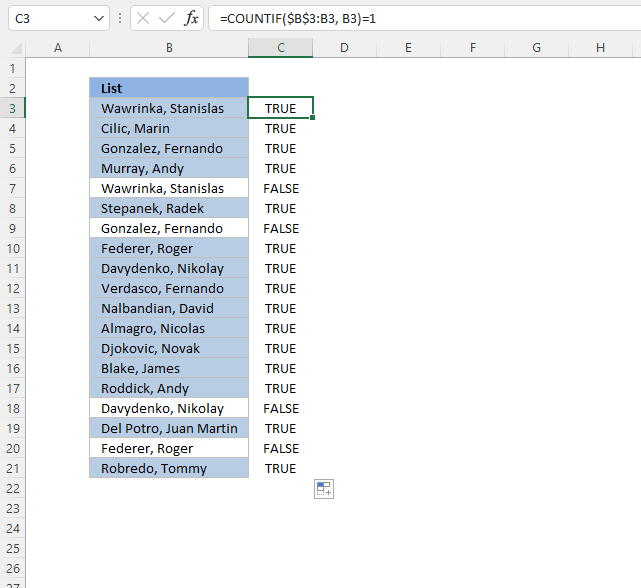
Stride i - COUNTIF function
The COUNTIF function has ii arguments, the starting time argument is the cell range you desire to count a specific value in. The 2nd argument is the value you want to count.
COUNTIF(range,criteria)
Step 2 - COUNTIF arguments
The starting time argument uses both relative and absolute jail cell references, $B$3:B3. The absolute part has dollar signs $B$3 pregnant information technology does not change when the Provisional Formatting formula is applied to the next jail cell.
The relative part B3 does change when the Conditional Formatting formula is applied to the adjacent cell.
COUNTIF($B$three:B3, B3)
Step three - Demonstrate calculations in cells B3 and B4
In cell B3 the office is COUNTIF($B$three:B3,B3)
and in cell B4: COUNTIF($B$three:B4,B4) and then on.
This technique using growing prison cell references lets you highlight the beginning example of a value but not duplicate values.
Step 4 - Compare output to one
How do we know if the value is a unique distinct value? Compare COUNTIF($B$three:B3,B3) to i and information technology will render True or False, like this:
COUNTIF($B$iii:B3,B3)=1
The equal sign is a logical operator that returns Truthful or FALSE. Note, the comparison is not case sensitive. The output is a boolean value Truthful or FALSE.
COUNTIF($B$three:B3,B3)=1
becomes
ane=one
and returns boolean value True. Cell B3 is highlighted.
If COUNTIF($B$3:B3,B3) returns a number larger than 1 meaning at that place is at least a duplicate value in the cell range specified in the start argument. That prevents the Conditional Formatting formula from highlighting the cell.
Recommended manufactures
Highlight unique/duplicates
Highlight current date
Highlight lookup values
Highlight cells equal to
iv.3 Sort Conditional formatted cells at the top
Tip! Press with correct mouse button on on a highlighted prison cell, press with left mouse button on Sort and then on "Put Selected Cell Color On pinnacle" to accommodate unique distinct values at the very top of your list.
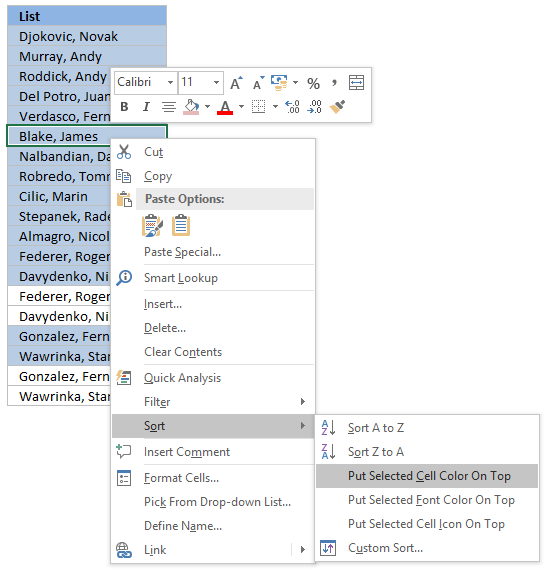
The picture below shows you all unique distinct values sorted together.
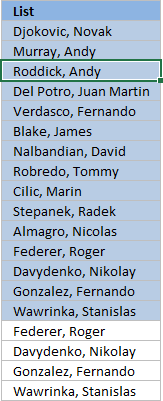
Dorsum to elevation
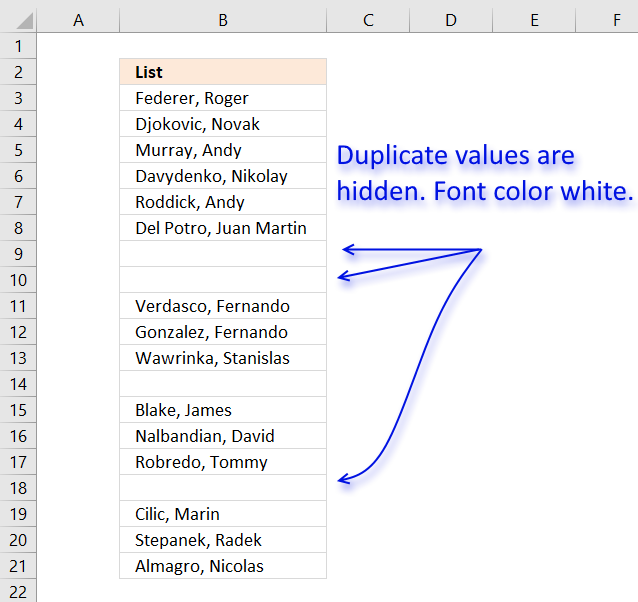
The image above demonstrates Conditional Formatting applied to a list of values, information technology changes the font color to white for duplicate values making them invisible or they appear hidden.
Keep in mind that the text is still in that location so if you copy the range and paste the values to a new range the hidden values are visible once more. I recommend that you sort the visible values at the peak in club to copy them correctly, instructions below.
Provisional Formatting formula:
=COUNTIF($B$iii, B3)>1
Back to top
How to apply conditional formatting formula to jail cell range B3:B21
- Select cell range B3:B21.
- Go to tab "Home" on the ribbon.
- Press with left mouse button on the "Conditional Formatting" button.
- Press with left mouse button on "New Rule..."
- Press with left mouse button on "Employ a formula to determine which cells to format:".
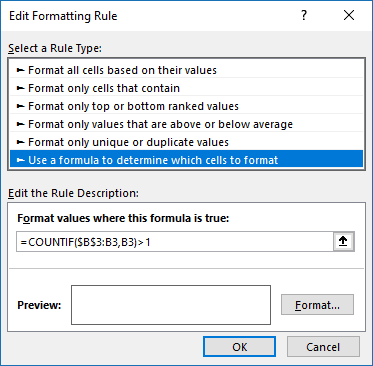
- Blazon the Conditional Formatting formula in "Format values where this is truthful:".
- Press with left mouse button on "Format..." button.
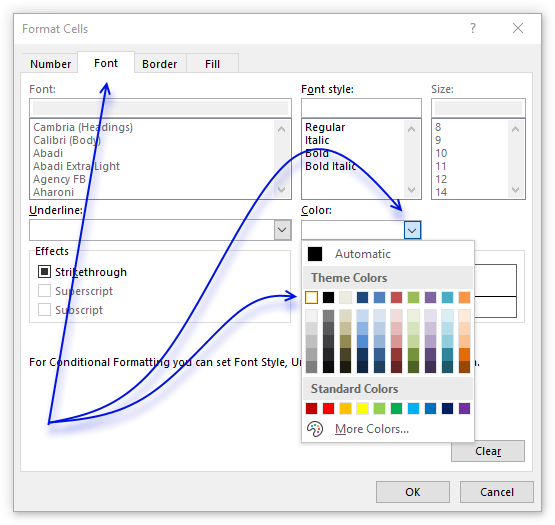
- Get to tab "Font" on the menu, see image to a higher place.
- Press with left mouse push on color driblet-down list.
- Pick white.
- Printing with left mouse push button on OK push button.
- Press with left mouse button on OK button.
- Press with left mouse push button on OK button.
Back to top
6. How to sort unique distinct values at the top of the list
- Printing with right mouse button on on one of the visible values in the listing.
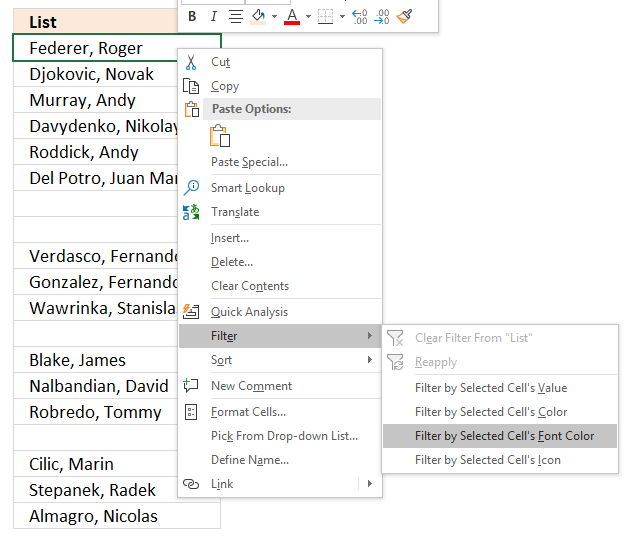
- Printing with left mouse button on "Filter"
- Press with left mouse push button on "Filter by Selected Cell'south Font color.
Recommended articles
Highlight unique values and unique distinct values in a multi-cavalcade cell range
Highlight unique distinct records
Highlight unique values in a filtered excel table
How to highlight indistinguishable values in a column
Check out the Conditional formatting category
Back to elevation
7. Extract unique singled-out sorted values from a jail cell range [UDF]
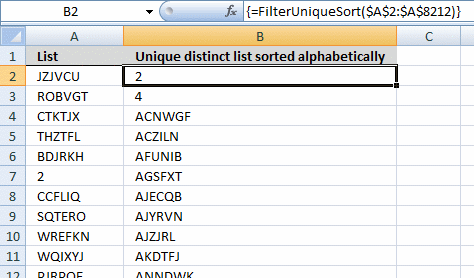
This UDF lets you create and sort a unique distinct listing. First yous need to re-create the VBA code to your workbook, instructions beneath. 2d, select a cell range. Third, blazon FilterUniqueSort(cell_ref) in the formula bar. Last, enter formula every bit an array formula, instructions below.
At that place is besides a workbook for y'all to get.
Assortment formula in prison cell B2:B8212:
=FilterUniqueSort($A$2:$A$8212)
7.1 Video
This video explains how to implement and use the User Defined Function
Subscribe to Go Digital Help on Youtube:
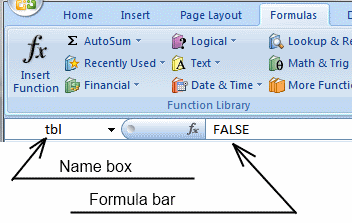
7.ii How to create an array formula
- Type B2:B8212 in name box
- Blazon higher up assortment formula in formula bar
- Press and concord Ctrl + Shift
- Printing Enter one time
- Release all keys
Recommended reading
A beginners guide to Excel array formulas
Back to superlative
seven.3 VBA code
I am using the selection sort function to sort values. You can read more about the function here:
Using a Visual Basic Macro to Sort Arrays in Microsoft Excel
'Proper name User Defined Part and define paremeter Function FilterUniqueSort(rng Every bit Range) 'Dimension variables and declare information types Dim ucoll As New Collection, Value Equally Variant, temp() As Variant Dim iRows Equally Unmarried, i Every bit Single 'Redimension array variable ReDim temp(0) 'Enable mistake treatment On Fault Resume Side by side 'Iterate through each value in range For Each Value In rng 'Check if number of characters in value is greater than 0 (zero), if true add value to collection ucoll If Len(Value) > 0 So ucoll.Add Value, CStr(Value) 'Proceed with next value Next Value 'Disable error treatment On Error GoTo 0 'Iterate through each value in drove ucoll For Each Value In ucoll 'Salvage value to last container in array variable temp temp(UBound(temp)) = Value 'Add together new container to assortment variable temp ReDim Preserve temp(UBound(temp) + 1) 'Next value Next Value 'Remove last container in array variable temp ReDim Preserve temp(UBound(temp) - i) 'Relieve selected rows on worksheet to variable iRows iRows = Range(Application.Caller.Address).Rows.Count 'Start User Defined Office SelectionSort with values in array variable temp SelectionSort temp 'Add blanks to array variable temp to prevent error values on worksheet For i = UBound(temp) To iRows 'Add container ReDim Preserve temp(UBound(temp) + ane) 'Save bare to container temp(UBound(temp)) = "" 'Continue with next value Next i 'Transpose values in array variable temp and return those values to worksheet FilterUniqueSort = Application.Transpose(temp) Cease Part
'Proper noun User Defined Function (UDF) and define parameters Role SelectionSort(TempArray As Variant) 'This UDF sorts values in an array 'https://world wide web.get-digital-help.com/how-to-extract-a-unique-list-and-the-duplicates-in-excel-from-i-column/#7.three 'Dimension variables and declare data types Dim MaxVal Equally Variant Dim MaxIndex Every bit Integer Dim i Every bit Integer, j As Integer 'Iterate through each value in array variable temp starting from concluding to first For i = UBound(TempArray) To 0 Step -i 'Salvage value to variable MaxVal MaxVal = TempArray(i) 'Salve value stored in variable i to variable MaxIndex MaxIndex = i 'Iterate through each value in array variable temp For j = 0 To i 'Check if value in array variable TempArray is larger than value stored in variable MaxVal 'Excel can compare text values besides, this action checks if a text value is before or after another value in a sorted list If TempArray(j) > MaxVal Then 'If true save value to variable MaxVal MaxVal = TempArray(j) 'Relieve position to MaxIndex MaxIndex = j End If 'Go along with adjacent value Next j 'Check if number stored in variable MaxIndex is smaller than number stored in variable i If MaxIndex < i And then 'Save value in array variable TempArray position i to array variable TempArray container position MaxIndex TempArray(MaxIndex) = TempArray(i) 'Salve value in variable MaxVal to array variable TempArray container position i TempArray(i) = MaxVal Stop If Side by side i Terminate Role
Back to top
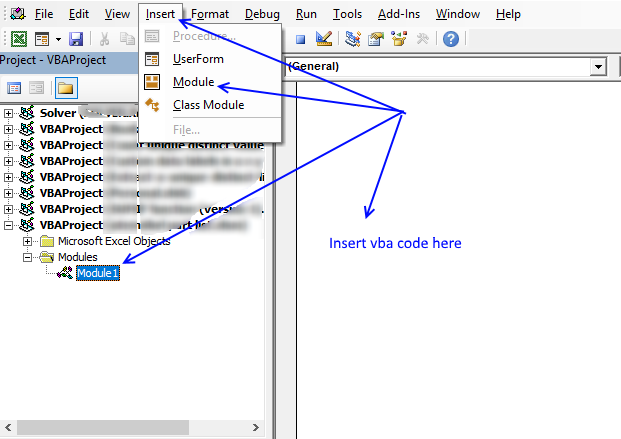
7.four Where to copy VBA code?
- Printing Alt + F11 to open up VB Editor
- Press with left mouse push on "Insert" on the bill of fare
- Printing with left mouse button on "Module" to create a module
- Copy (Ctrl + c) above VBA code and paste (Ctrl +v) to the code module
Dorsum to top
More powerful User Defined Functions
Filter unique singled-out records (case sensitive) [UDF]
Lookup and render multiple values concatenated into 1 cell
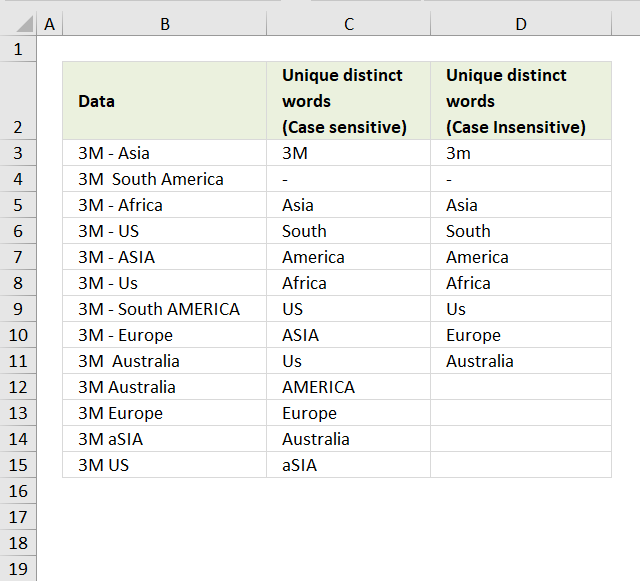
Filter unique distinct words from a cell range [UDF]
Dorsum to acme
8. Filter unique distinct values from multiple sheets add together-in
Filter unique distinct valuesis an add-in for Excel 2007/2010/2013 that lets you excerpt
- unique distinct values
- duplicate values
- unique distinct records
- duplicate records
from multiple sheets. The Add-In contains 4 user-divers functions.
If a value in one of the ranges changes the role will automatically and instantly update the list.
Features
- All user-defined functions remove blank values and bare records.
- No fault values when all values are extracted.
- Filter values or records from upward to 255 different prison cell ranges or sheets.
8.one Watch this video where I demonstrate the Excel Add-In
Subscribe to Get Digital Aid on Youtube:
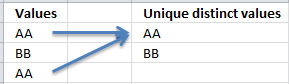
What are unique distinct values?
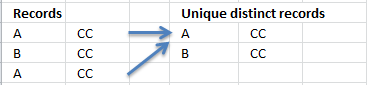
What are unique distinct records?
Purchase Filter Unique Singled-out Values From Multiple Sheets Add-in For Excel 2007/2010/2013 - Price $19 USD
Questions
Is there a coin back guarantee?
Sure, you lot have a unconditional money dorsum guarantee for 14 days.
Back to top
9. Create a list of unique distinct values [Old array Formula]
I recommend using the regular formula in a higher place since it is smaller and has an advantage of not being an array formula.

Array formula in jail cell D3:
=INDEX($B$three:$B$21, MATCH(0, COUNTIF($D$ii:D2, $B$3:$B$21), 0))
Thanks to Eero, who contributed the original array formula!
Back to top
The formulas above has an outcome with blank cells, it returns a 0 (zero) in your listing. This article shows you how to ignore blanks:
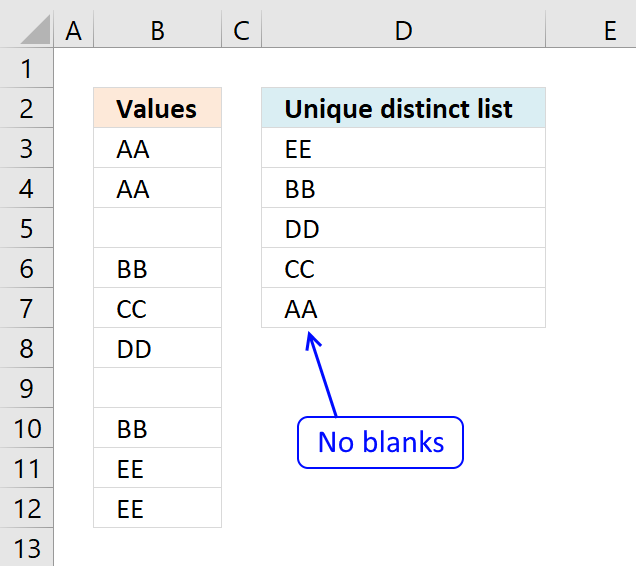
Extract a unique distinct listing and ignore blanks
9.1 How to create an assortment formula
You lot don't need to follow these steps if y'all chose the regular formula.
- Re-create the array formula above (Ctrl + c)
- Double press with left mouse push button on cell B2
- Paste (Ctrl + v)
- Press and concur Ctrl + Shift simultaneously
- Printing Enter
- Release all keys
If you made the in a higher place steps correctly the formula now has a beginning and ending curly bracket, similar this:
{=Index($B$3:$B$21, MATCH(0, $D$2:D2, $B$3:$B$21), 0))}
Don't enter these characters yourself, they appear automatically.
Re-create cell B2 and paste to cells below equally far equally needed.
Dorsum to top
nine.2 How the assortment formula in jail cell B2 works
Step 1 - Create an array with the aforementioned size every bit the listing
The COUNTIF function calculates the number of cells equal to a condition.
COUNTIF(range,criteria)
COUNTIF($B$i:B1, $A$2:$A$twenty)
becomes
COUNTIF("Unique distinct listing",{Federer,Roger; Djokovic,Novak; Murray,Andy; Davydenko,Nikolay; Roddick,Andy; DelPotro,JuanMartin; Federer,Roger; Davydenko,Nikolay; Verdasco,Fernando; Gonzalez,Fernando; Wawrinka,Stanislas; Gonzalez,Fernando; Blake,James; Nalbandian,David; Robredo,Tommy; Wawrinka,Stanislas; Cilic,Marin; Stepanek,Radek; Almagro,Nicolas} )
and returns:
{0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0}
This ways the cell value in $B$one:B1 can't be found in any of the cells in cell range $A$ii:$A$twenty. If it had been found, somewhere in the assortment the number one would exist.
Step ii - Render the position of an item that matches 0 (nothing)
The Lucifer function returns the relative position of an item in an assortment that matches a specified value.
Friction match(lookup_value, lookup_array, [match_type]
MATCH(0, COUNTIF($B$1:B1, $A$2:$A$twenty), 0)
becomes
Friction match(0,{0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0},0)
and returns 1.
Step 3 - Return a jail cell value
The Alphabetize function returns a value or reference of the cell at the intersection of a particular row and cavalcade, in a given range.
INDEX(array, row_num, [column_num])
Alphabetize($B$iii:$B$21, 1)
becomes
=Index({Federer,Roger; Djokovic,Novak; Murray,Andy; Davydenko,Nikolay; Roddick,Andy; DelPotro,JuanMartin; Federer,Roger; Davydenko,Nikolay; Verdasco,Fernando; Gonzalez,Fernando; Wawrinka,Stanislas; Gonzalez,Fernando; Blake,James; Nalbandian,David; Robredo,Tommy; Wawrinka,Stanislas; Cilic,Marin; Stepanek,Radek; Almagro,Nicolas}, ane)
and returns "Federer, Roger".
Relative and accented prison cell references
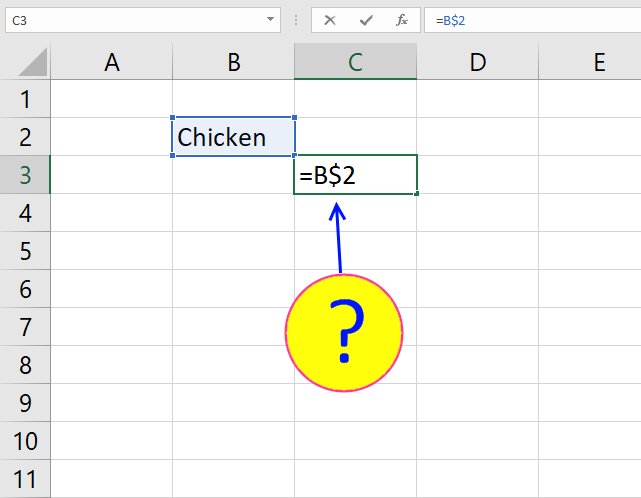
When you re-create the array formula down the countif formula range ($B$i:B1) expands. This is created by using relative and accented references.
The beginning prison cell, B2: COUNTIF($B$one:B1,$A$two:$A$20)
Second jail cell, B3: COUNTIF($B$ane:B2,$A$2:$A$xx)
and and so on.
Recommended reading:
How to use absolute and relative references
Dorsum to top
10. How to filter unique values from a listing
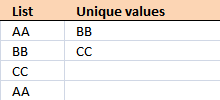
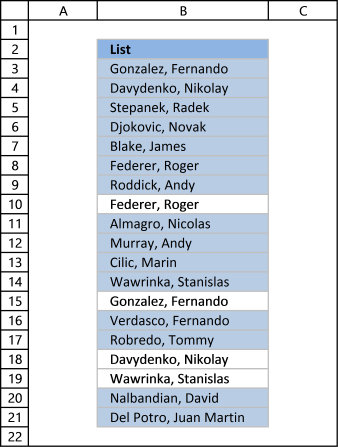
Unique values are values existing merely once in a list. Example, "AA" exists twice in the listing beneath and is not unique. BB and CC exist just once each and are unique in the list.
Column D in the picture below filters all unique values from column B. Unique values are values that exist only once in column B.
Example, Roger, Federer is non in column D considering there is more than ane value of this proper name in column A. In other words, the proper name is not unique in column A. You can notice the name twice in the list, in cells A2 and A8.
Update 2017-08-30
This formula is even smaller than the array formula and you are not required to enter this as an array formula.
Regular formula in prison cell D3:
=LOOKUP(ii, ane/((COUNTIF(D2:$D$2, $B$iii:$B$21)=0)*(COUNTIF($B$3:$B$21, $B$3:$B$21)=one)), $B$iii:$B$21)
Recommended articles
How to excerpt a instance sensitive unique list from a column
Filter unique values sorted from A to Z
Extract unique values from two columns
Update 2020-12-09, the formula below extracts unique values from prison cell range $B$three:$B$21:
Regular formula in cell D3:
=UNIQUE($B$three:$B$21,,Truthful)
The formula above contains the new UNIQUE function that only Excel 365 subscribers tin use. Use the formula above if you have an earlier Excel version.
Recommended manufactures
Extract unique values - Excel 365 (Link)
Extract unique values sorted from A to Z - Excel 365 (Link)
Extract unique values ignoring blanks - Excel 365 (Link)
Extract unique values sorted from A to Z ignoring blanks - Excel 365 (Link)
Array formula in cell D3:
=INDEX($B$3:$B$21, MATCH(0, COUNTIF(D2:$D$2, $B$3:$B$21)+(COUNTIF($B$3:$B$21, $B$3:$B$21)<>1), 0))
How to enter an assortment formula
Back to top
x.ane Explaining array formula in cell D3
Step one - Count each value in array and cheque if it is not equal to one
(COUNTIF($A$two:$A$xx, $A$2:$A$20)<>1
becomes
{2;1;1;ii;1;i;ii;two;1;two;two;2;i;1;1;2;1;one;ane}<>1
and returns
{TRUE; FALSE; Imitation; Truthful; Simulated; FALSE; Truthful; TRUE; FALSE; True; True; TRUE; Fake; FALSE; Faux; TRUE; Fake; FALSE; FALSE}
This array tells excel that the first value in the assortment is not unique and that is true considering Roger, Federer is non unique in the list. Notwithstanding the 2nd value is FALSE and that value is unique, etc.

How to apply the COUNTIF function
Step 2 - Keep track of previous values
C1:$C$1 is a dynamic jail cell reference, it changes equally the formula is copied to cells below. You can read more about absolute and relative prison cell references here:

How to use absolute and relative references
COUNTIF(C1:$C$1, $A$2:$A$xx)
becomes
COUNTIF("Unique list", {"Federer, Roger "; "Djokovic, Novak "; "Murray, Andy "; "Davydenko, Nikolay "; "Roddick, Andy "; "Del Potro, Juan Martin "; "Federer, Roger "; "Davydenko, Nikolay "; "Verdasco, Fernando "; "Gonzalez, Fernando "; "Wawrinka, Stanislas "; "Gonzalez, Fernando "; "Blake, James "; "Nalbandian, David "; "Robredo, Tommy "; "Wawrinka, Stanislas "; "Cilic, Marin "; "Stepanek, Radek "; "Almagro, Nicolas "})
and returns
{0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0}
A zero (0) means that no values have nevertheless been displayed and that is true in cell C2. However when excel calculates the value in cell C3, jail cell C2 shows "Djokovic, Novak" and the array becomes {0; ane; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0}. The second value in the array contains 1. This tells excel that value has already been shown.
Footstep 3 - Add arrays
COUNTIF(C1:$C$one, $A$2:$A$twenty)+(COUNTIF($A$2:$A$20, $A$2:$A$20)<>ane
becomes
{True; FALSE; FALSE; TRUE; Faux; False; TRUE; True; FALSE; Truthful; Truthful; Truthful; Fake; Fake; FALSE; True; Simulated; FALSE; Fake} + {0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0; 0}
and returns
{ane;0;0;i;0;0;1;ane;0;1;1;one;0;0;0;1;0;0;0}
True is 1 and FALSE is zero. And then True + 0 equals 1 and False + 1 equals 1.
Step 4 - Find first zero value in array
A nix in the array indicates {1;0;0;1;0;0;ane;one;0;1;1;ane;0;0;0;1;0;0;0} that the respective value is unique and has not yet been displayed in the list.
Match(0, COUNTIF(C1:$C$1, $A$2:$A$xx)+(COUNTIF($A$2:$A$20, $A$2:$A$20)<>1), 0)
becomes
Match(0, {ane;0;0;1;0;0;1;1;0;1;one;one;0;0;0;1;0;0;0}, 0)
and returns two.

How to use the Match function
Step 5 - Return respective value
Alphabetize($A$two:$A$twenty, MATCH(0, COUNTIF(C1:$C$1, $A$2:$A$20)+(COUNTIF($A$2:$A$20, $A$2:$A$twenty)<>1), 0))
becomes
Alphabetize($A$2:$A$20, ii)
and returns "Djokovic, Novak" in cell C2.

How to use the INDEX function
Back to summit
10.2 Get Excel file
To extract duplicates, see this mail:
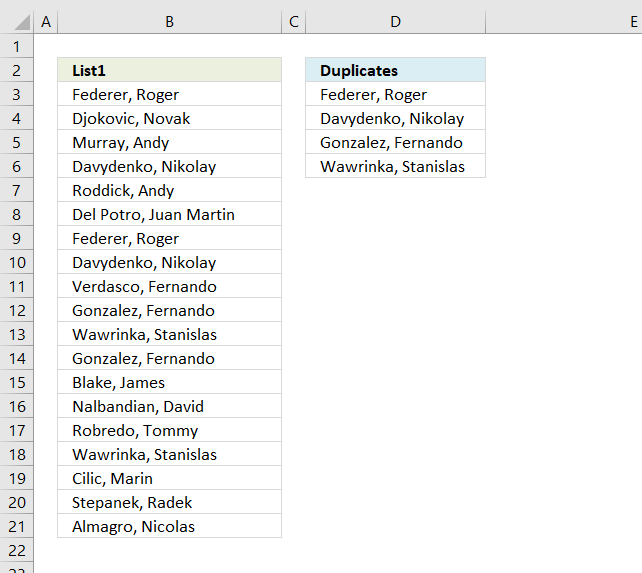
Excerpt a list of duplicates from a cavalcade
Dorsum to top
eleven. Highlight unique values [Conditional Formatting]
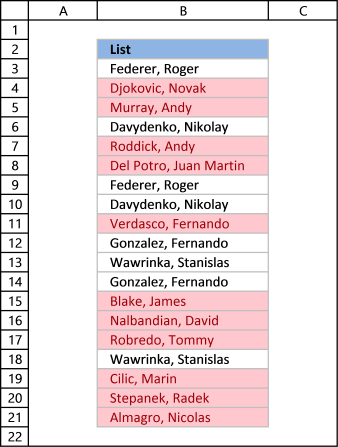
This example demonstrates how to highlight cells with a colour of your pick if it contains a unique value.
xi.ane Video
The post-obit video shows y'all how to colour unique values using provisional formatting. Recollect, information technology highlights merely unique values, in other words, values that be only one time in the list.
Subscribe to Become Digital Assistance on Youtube:
Instructions
- Go to tab "Home" on the ribbon
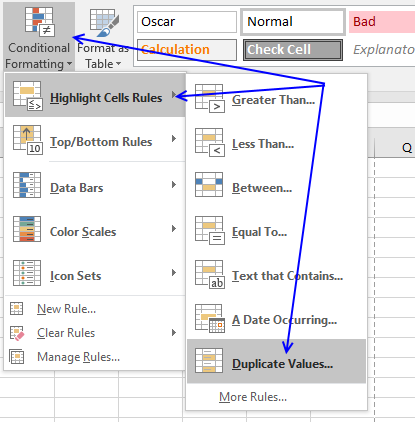
- Printing with left mouse button on "Conditional Formatting" button
- Hover over "Highlight Cell Rules"
- Printing with mouse on "Duplicate Values..."
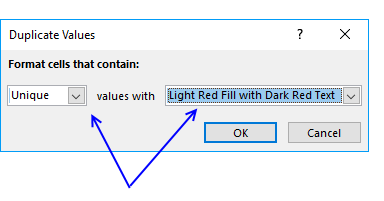
- Printing with mouse on the leftmost driblet-down list and change it to "Unique"
- Pick a formatting if you like
- Press with left mouse push on OK push button

The film above shows you, for case, that the first proper noun in the listing has a duplicate and then that name is not highlighted in any cell.
11.ii Sort unique values at the summit
Tip! Did you lot know that you can put highlighted values to the tiptop
- Printing with right mouse button on on a highlighted prison cell
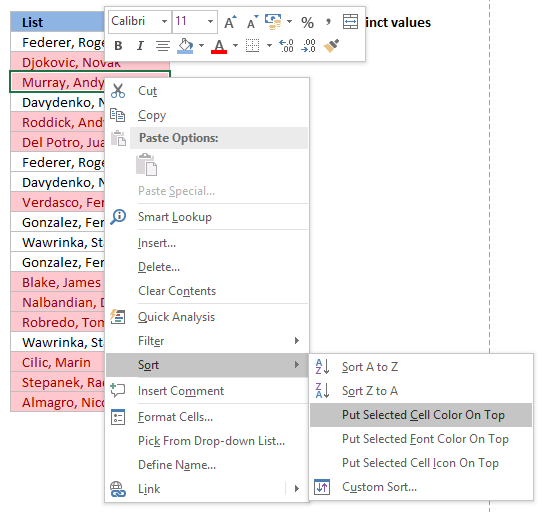
- Press with mouse on "Sort"
- Press with mouse on "Put Selected Cell Color On Height"
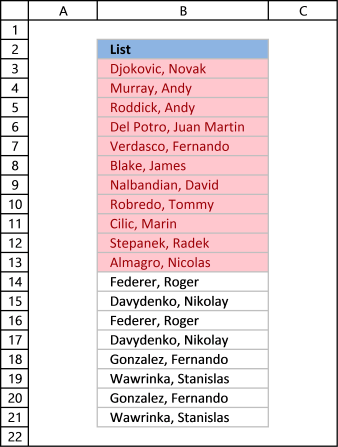
Back to meridian
12. Useful tips
12.1 Excel tables
An Excel Table is a dandy characteristic and is very cleverly designed. It is synthetic to automatically expand if you lot add more data which is incredibly helpful. You don't need to practice anything, not adjusting cell references which is time consuming and prone to errors.
Structured references are prison cell references to an excel divers tabular array. They allow you lot easily come across what the data contains equally long as yous give information technology expert descriptive column header names.
I recommend you lot apply excel defined tables instead of named ranges or dynamic named ranges as long as you are working with more than than one value.
Here is how to convert a list to an excel defined table:
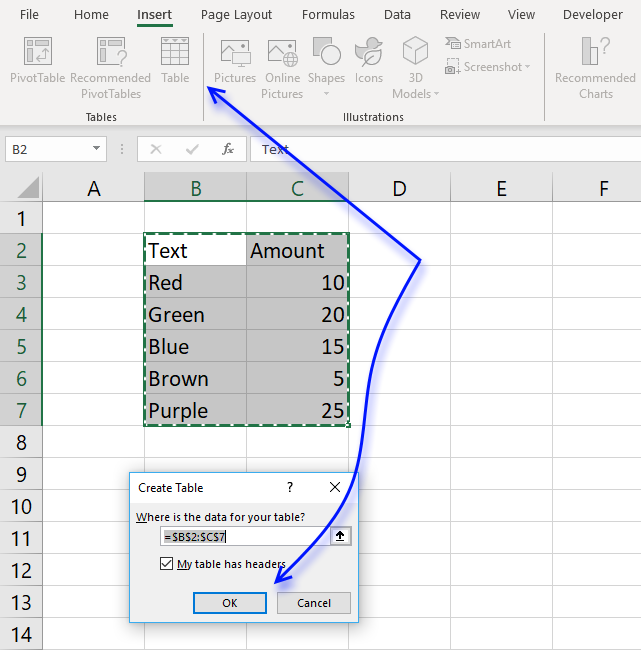
- Select a prison cell in your listing
- Go to tab "Insert" on the ribbon and press with left mouse push on Table push or printing Ctrl + T
- Press with left mouse push on OK button
- Your excel defined tabular array is created
Read more about excel defined tables
Back to top
12.ii Named ranges
In excel you tin name a jail cell range, a constant or a formula. You lot tin can and then employ the named range in a formula, making information technology easier for you to read and understand formulas.
Case
List : A2:A20
Tip! Use dynamic named ranges to automatically adjust cell ranges when new values are added or removed.
12.2.ane How to create a named range
The downside with named ranges is that you need to adjust the range every fourth dimension you add or delete a value in the list, the named range will and so not fit the value list. I recommend using excel divers tables if you know that the list may modify in the hereafter.
- Select prison cell range B3:B7
- Type Colorin name box
- Press Enter
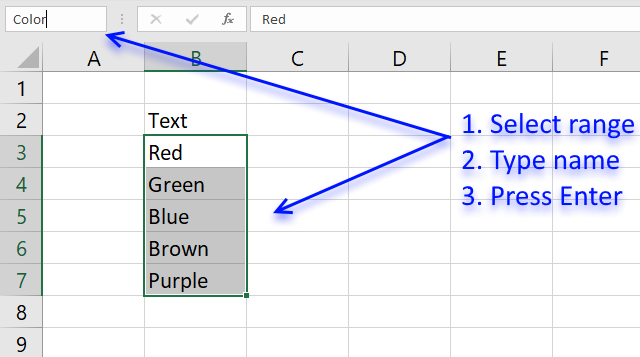
Formula example containing proper noun range:
=Index(Color,MATCH(0,COUNTIF($C$ii:C2,Color),0))
Back to top
13. How to remove errors (Excel 2007)
Excel 2007 users (and later versions) can remove errors using IFERROR() function.
When the formula runs out of values it returns #Northward/A errors (Non Available), you lot can use the IFERROR function to remove the error and return blanks in those cells.
Unfortunately, it comes with a large disadvantage, information technology likewise removes other formula errors as well. So employ this with great caution. If your source table has errors you won't detect information technology because the IFERROR function returns a blank cell instead.
Array formula in cell D2:
=IFERROR(LOOKUP(two, 1/(COUNTIF($D$two:D2, $B$3:$B$21)=0), $B$3:$B$21), "")
and copy it down every bit far every bit necessary.
Dorsum to meridian
Recommended manufactures
How to use the IFERROR function
How to employ the ISERROR function
How to use the ERROR.TYPE function
How to find errors in a worksheet
Delete blanks and errors in a list
Dorsum to top
fourteen. Excel 2003 users can remove errors using isna() function:
=IF(ISNA(Alphabetize($A$2:$A$20, MATCH(0, COUNTIF($B$i:B1, $A$2:$A$20), 0))), "", Index($A$2:$A$20, Lucifer(0, COUNTIF($B$1:B1, $A$2:$A$20), 0)))
and copy information technology down as far as needed.
This formula is an assortment formula, how to enter an array formula.
Recommended commodity
- ISNA function
Back to top
xv. How to ignore bare cells in a range
Harlan Grove created a formula to count unique distinct values from a list with blanks. I used the same technique here to filter unique singled-out values in column D.
If yous want a header proper noun y'all can use the slightly larger formula, displayed in cavalcade F below.
Update 2020-12-09, Excel 365 users can use this regular formula:
=UNIQUE(FILTER($B$3:$B$21, ($B$three:$B$21<>"") * ($B$3:$B$21<>"")))
The formula below is actually 58 character while the new Excel 365 formula above is 61 characters, infinite characters non included. You lot can find a formula explanation here: Excerpt unique distinct values ignoring blanks
Utilise the formula beneath if yous have an earlier Excel version than Excel 365.
Update 2017-09-01, smaller regular formula in cell D3:
=LOOKUP(two, i/(COUNTIF($D$two:D2, $B$iii:$B$21&"")=0), $B$3:$B$21)
Formula in cell F3 if you need a cavalcade header proper noun:
=LOOKUP(two, 1/((COUNTIF($F$2:F2, $B$3:$B$21)+($B$3:$B$21=""))=0), $B$3:$B$21)
15.1 Sentry a video where I explain how these ii formulas work
Subscribe to Get Digital Help on Youtube:
This article shows you lot how to fill blank cells with values or formulas
Acquire how to extract non-blank cells in a list using a formula:
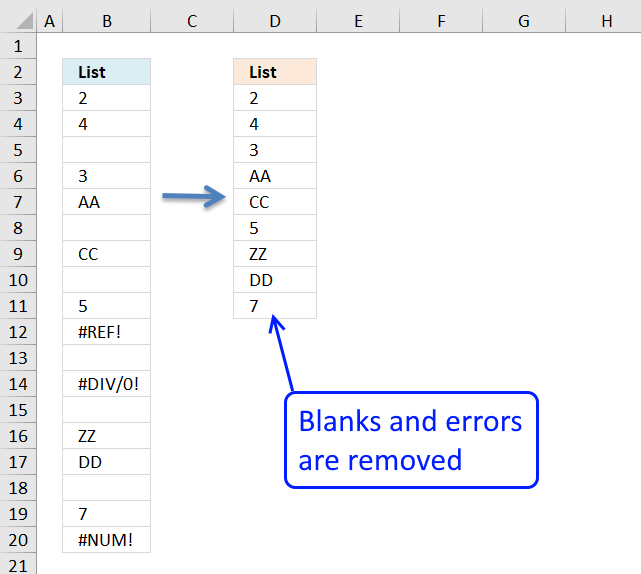
Remove blank cells
In this web log post I will provide 2 solutions on how to remove blank cells and a solution on how […]
Remove blank cells
Back to superlative
15.2 Get Excel file
Back to top
Source: https://www.get-digital-help.com/how-to-extract-a-unique-list-and-the-duplicates-in-excel-from-one-column/
Posted by: faydoely1954.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Excel How To Find Unique Values In A List"
Post a Comment