How To Find The Upper And Lower Fence
Descriptive Statistics > Upper and Lower Fence
What are upper and lower fences?
Upper and lower fences cordon off outliers from the bulk of data in a set. Fences are ordinarily plant with the following formulas:
- Upper fence = Q3 + (1.5 * IQR)
- Lower fence = Q1 – (one.5 * IQR).
Where IQR is the interquartile range. Sometimes the value 1.5 is replaced past some other value (usually 3), but you'll commonly encounter ane.5 unless yous're calculating inner and outer fences.
Inner and Outer Fences
Fences can be used to illustrate extreme values (outliers) in box plots. Sometimes yous might see reference to "inner fences" and "outer fences". These are divers as:
- Lower inner argue: Q1 – (one.five * IQR)
- Upper inner fence: Q3 + (one.5 * IQR)
- Lower outer fence: Q1 – (three * IQR)
- upper outer fence: Q3 + (three * IQR)
Points beyond the inner fences in either direction are mild outliers; points beyond the outer fences in either management are farthermost outliers.
Need assistance with a homework question? Cheque out our tutoring page!
Example:
Which of the following data points are outliers?
29, 179, 180, 201, 300, 301, 304, 350, 399, 401, 455, 501, 503, 540, 543, 549, 560, 561, 562, 563, 569, 570, 599, 601, 603, 650, 701, 703, 704, 709, 713, 733, 745, 801, 900, 982, 983, 985, 999, 1001, 1002, 1003, 1009, 1100, 1101, 1102, 1103, 1109, 1201, 1301, 1399, 1400, 1501, 1599, 1699.
Step ane: Observe the 25th percentile (Q1), the 75th percentile (Q3), and the interquartile range. Our interquartile range calculator can do this for you, or if yous want to summate these manually, meet How to Observe an Interquartile Range for step past step instructions (with video). From the calculator, we go:
- 25th Percentile: 540
- 75th Percentile: 1003
- Interquartile Range: 463
Footstep 2: Insert the values from Footstep 1 into the formulas and solve:
- Lower inner fence: Q1 – (i.5 * IQR) = 540 – (1.5 * 463) = -154.5
- Upper inner fence: Q3 + (ane.5 * IQR) = 1003 + (1.v * 463) = 1697.5
- Lower outer debate: Q1 – (3 * IQR) = 540 – (3 * 463) = -849
- upper outer fence: Q3 + (3 * IQR) = 1003 + (3 * 463) = 2392
Step 3: Plot the upper and lower fences on a box plot. Non necessarily statistically, just it makes outliers easier to spot:
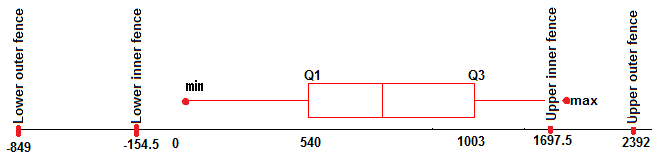
Only one indicate (1699) is an outlier, considering information technology lies outside the fences. As it'due south over the upper inner fence but not over the upper outer fence, it's considered a mild outlier.
The definitions for the outer and inner fences only represent the maximum value where the whiskers could go, if the data prepare really independent those values. In other words, the whiskers don't extend to the fences unless in that location are actual data points at those places. Whiskers represent data points; Fences represent theoretical cut-off points.
References:
Everitt, B. S.; Skrondal, A. (2010), The Cambridge Dictionary of Statistics, Cambridge Academy Press.
Tukey, J. (1977). Exploratory Information Analysis, Addison-Wesley.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Demand aid with a homework or examination question? With Chegg Study, you lot can become stride-past-step solutions to your questions from an expert in the field. Your showtime 30 minutes with a Chegg tutor is complimentary!
Comments? Need to post a correction? Please post a comment on our Facebook page .
How To Find The Upper And Lower Fence,
Source: https://www.statisticshowto.com/upper-and-lower-fences/
Posted by: faydoely1954.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find The Upper And Lower Fence"
Post a Comment